
AFFO, or adjusted funds from operations, is a REIT valuation measure that helps investors determine the profitability of a REIT. This measure is calculated based on the income and expenses of a real estate investment. It is calculated by subtracting the amount of capital expenditures and interest income that a REIT may incur on its properties. It also calculates the REIT’s potential dividend-paying power. It is a non-GAAP measure and should be used in conjunction with other metrics to determine a REIT's performance.
AFFO provides a better indicator of a REIT’s cash income than net income. However, AFFO cannot be used to replace free cash flow. It should be used to evaluate the growth potential for a REIT. It is also a better indicator of a REIT’s dividend potential. The AFFO payout ratio (AFRO) of 100 is the AFFO. This ratio is calculated as a subtraction of the average AFFO return for a period. This ratio can be calculated by dividing each REIT's average yield in the period by their average AFFO-yield.

FFO is the most widely used valuation measure for REITs. It is a nonGAAP financial measure which shows the REIT’s liquidity generation. It can be found on the REIT’s income statements or cash flow statements. FFO includes amortization and depreciation. It excludes gains and losses from the sale of depreciable property and one-time expenses. It also includes adjustments made for unconsolidated partnership and joint ventures.
FFO is a good measure of a REIT's net cash generation, but it does not give a full picture of a REIT's recurring cash flow. Net income for a REIT can be calculated by subtraction of the income statement's income. This figure is usually listed in the footnotes. It can be calculated as a percentage or per-share.
The average FFO/price ratio in the first quarter 2016 was 17.3, which is down from 19.7 and 22 respectively in 2015 and 2015. REITs of the first quarter provided a 10-percentage-point premium over the constrained portfolio. In 1Q15, however, all quartiles exceeded that of the REIT Index. The gap has widened slightly over the long-term. It is worth looking closely at the properties that a REIT owns to get a more accurate picture of the company’s performance.
FFO can also be calculated per share, per quarter, or per year. However, most REITs use the FFO method to offset their cost accounting methods. FFO per share can also be used by companies as an addition to EPS. A close look at the income statement of a specific REIT can provide more accurate information.
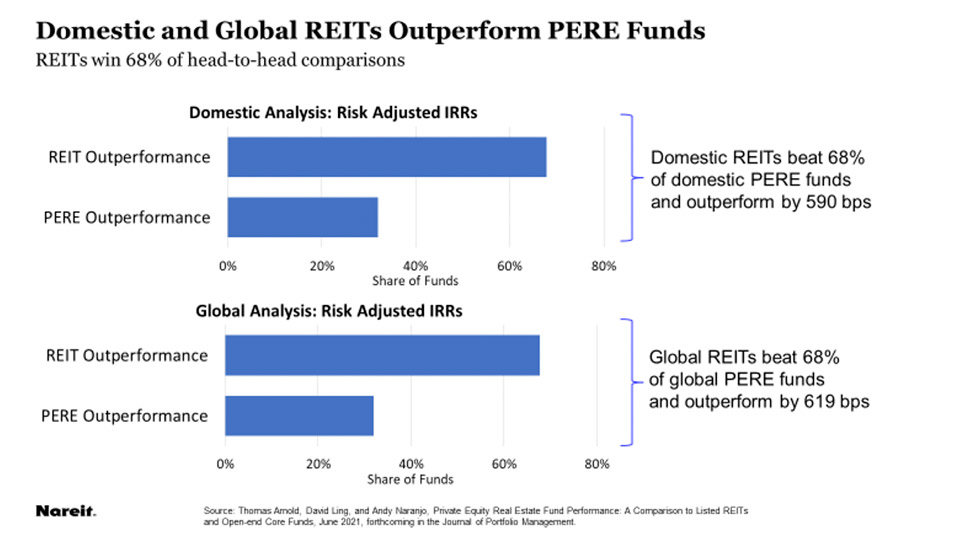
FFO and AFFO are two of the most common metrics used to evaluate REITs. They can't be used interchangeably. They should be used in conjunction with other metrics to gauge the REIT's performance and profitability. The P/FFO ratio is also a valuable tool for evaluating a REIT's management.
FAQ
What is a bond?
A bond agreement is an agreement between two or more parties in which money is exchanged for goods and/or services. It is also known as a contract.
A bond is usually written on paper and signed by both parties. This document includes details like the date, amount due, interest rate, and so on.
The bond is used for risks such as the possibility of a business failing or someone breaking a promise.
Bonds are often combined with other types, such as mortgages. This means that the borrower has to pay the loan back plus any interest.
Bonds can also help raise money for major projects, such as the construction of roads and bridges or hospitals.
The bond matures and becomes due. That means the owner of the bond gets paid back the principal sum plus any interest.
Lenders are responsible for paying back any unpaid bonds.
What is the trading of securities?
The stock market is an exchange where investors buy shares of companies for money. Companies issue shares to raise capital by selling them to investors. Investors can then sell these shares back at the company if they feel the company is worth something.
Supply and demand are the main factors that determine the price of stocks on an open market. When there are fewer buyers than sellers, the price goes up; when there are more buyers than sellers, the prices go down.
There are two ways to trade stocks.
-
Directly from company
-
Through a broker
What is the difference in marketable and non-marketable securities
The key differences between the two are that non-marketable security have lower liquidity, lower trading volumes and higher transaction fees. Marketable securities, on the other hand, are traded on exchanges and therefore have greater liquidity and trading volume. Because they trade 24/7, they offer better price discovery and liquidity. However, there are many exceptions to this rule. Some mutual funds are not open to public trading and are therefore only available to institutional investors.
Non-marketable securities can be more risky that marketable securities. They typically have lower yields than marketable securities and require higher initial capital deposit. Marketable securities are generally safer and easier to deal with than non-marketable ones.
A large corporation may have a better chance of repaying a bond than one issued to a small company. This is because the former may have a strong balance sheet, while the latter might not.
Because they can make higher portfolio returns, investment companies prefer to hold marketable securities.
What's the difference between the stock market and the securities market?
The securities market refers to the entire set of companies listed on an exchange for trading shares. This includes stocks, options, futures, and other financial instruments. Stock markets can be divided into two groups: primary or secondary. The NYSE (New York Stock Exchange), and NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) are examples of large stock markets. Secondary stock market are smaller exchanges that allow private investors to trade. These include OTC Bulletin Board Over-the-Counter, Pink Sheets, Nasdaq SmalCap Market.
Stock markets are important as they allow people to trade shares of businesses and buy or sell them. The value of shares is determined by their trading price. Public companies issue new shares. Investors who purchase these newly issued shares receive dividends. Dividends are payments made by a corporation to shareholders.
Stock markets serve not only as a place for buyers or sellers but also as a tool for corporate governance. Boards of directors are elected by shareholders to oversee management. They ensure managers adhere to ethical business practices. If a board fails to perform this function, the government may step in and replace the board.
What is security in the stock exchange?
Security can be described as an asset that generates income. Most security comes in the form of shares in companies.
One company might issue different types, such as bonds, preferred shares, and common stocks.
The earnings per shares (EPS) or dividends paid by a company affect the value of a stock.
Shares are a way to own a portion of the business and claim future profits. If the company pays you a dividend, it will pay you money.
You can sell your shares at any time.
Statistics
- Ratchet down that 10% if you don't yet have a healthy emergency fund and 10% to 15% of your income funneled into a retirement savings account. (nerdwallet.com)
- US resident who opens a new IBKR Pro individual or joint account receives a 0.25% rate reduction on margin loans. (nerdwallet.com)
- For instance, an individual or entity that owns 100,000 shares of a company with one million outstanding shares would have a 10% ownership stake. (investopedia.com)
- The S&P 500 has grown about 10.5% per year since its establishment in the 1920s. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to create a trading strategy
A trading plan helps you manage your money effectively. It helps you identify your financial goals and how much you have.
Before you begin a trading account, you need to think about your goals. It may be to earn more, save money, or reduce your spending. If you're saving money you might choose to invest in bonds and shares. If you're earning interest, you could put some into a savings account or buy a house. Perhaps you would like to travel or buy something nicer if you have less money.
Once you have a clear idea of what you want with your money, it's time to determine how much you need to start. This will depend on where you live and if you have any loans or debts. You also need to consider how much you earn every month (or week). Income is the sum of all your earnings after taxes.
Next, make sure you have enough cash to cover your expenses. These include rent, bills, food, travel expenses, and everything else that you might need to pay. These expenses add up to your monthly total.
You'll also need to determine how much you still have at the end the month. This is your net discretionary income.
This information will help you make smarter decisions about how you spend your money.
Download one from the internet and you can get started with a simple trading plan. You could also ask someone who is familiar with investing to guide you in building one.
Here's an example: This simple spreadsheet can be opened in Microsoft Excel.
This graph shows your total income and expenditures so far. It also includes your current bank balance as well as your investment portfolio.
Here's an additional example. This was created by a financial advisor.
It will help you calculate how much risk you can afford.
Remember, you can't predict the future. Instead, be focused on today's money management.